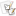Potential Regions of the Nuclear and Mitochondrial Genome for Characterization of Phytophthora species Schena L, Cooke DE. 2006 Assessing the potential of regions of the nuclear and mitochondrial genome to develop a J. Microbiological Methods 67:70-85 (pdf of reprint) The manuscript by Schena and Cooke (2006) described three mitochondrial and two nuclear regions of the genome where sequence variation could be used to differentiate species and in some cases, subpopulations of species. Some of these regions also are useful for developing diagnostic molecular markers for detection of particular species. A graphical overview of these regions and the primers used to amplify them may be found below. MitochondrialThere were three regions of the mitochondrial genome that were examined: Spacer and tRNAs between rpl5 and Rns gene Primers were designed for amplification of to regions from this area: TrnG to TrnY · This region was amplified from 25 species and was between 250 and 290 bp in length TrnY to Rns · Amplified 35 isolates representing 24 species Spacer region between cox1 and cox2 · Amplified from 27 species with a size ranging from 387 to 428 bp NOTE: the primers IgCoxF and IgCoxR listed in Table 2 of Schena and Cooke (2006) are essentially the same as FMPhy-8b and FMPhy-10b previously reported by Martin et al. (2004) for amplification of a Phytophthora genus-specific fragment in a field diagnostic assay for P. ramorum and several other species. The only difference was that two degenerations were introduced in IgCoxF. When amplifying field samples under high stringency there are several species that FMPhy-8b and FMPhy-10b will not amplify, but under reduced stringency with culture extracted DNA all Phytophthora species were found to amplify. More information on this primer pair and an alignment of this spacer region for all described Phytophthora species can be found Here. A greater degree of intraspecific polymorphisms has been observed in this region than previously observed (Martin et al. 2004). Spacer region between atp9 and nad9 · Amplified from 17 species with a size ranging from 322 to 355 bp Nuclear There were two regions of the nuclear genome that were examined: The introns in the ras-related protein Ypt1 · Additional work has been done on this region on the development of genus and species-specific primers subsequent to the publication of Schena and Cooke (2006); additional details for this region can be found here. A portion of the intergenic spacer region (IGS) of the rDNA repeat unit · Amplified from 28 species using a combination of 5 primers with a size ranging from 382 to 526 bp Figure 1 of Schena and Cooke (2006) Table 2 from Schena and Cooke, 2006 |